=======
Learning Covenant C2 - Setup Guide & Lessons learned
45 minute read - Published: 22 Dec, 2023
Section 0: Introduction
> In this guide, I'll show you how to set up Covenant C2 and establish your first listener in under an hour.
> Why am I writing this? My initial experience with configuring .NET and installing dependencies offline turned out to be more time-consuming than necessary. That being said, my mission is to spare you this hassle and provide a no-nonsense, straightforward tutorial to streamline your setup process.
> As my focus will be to show you what to look out for when installing offline, I'll also walk through setting up on a Kali machine with internet access.
> As a final note, I'll admit I am still new to red teaming, so I've designed this guide is for those who are also absolute beginners and new command and control (C2) tools.
Section 1: Technology Overview
> Description: Covenant C2 is a command and control (C2) post-exploitation framework. As of mid-September 2019, Covenant is considered one of the latest and advanced frameworks in this area.
> Prerequisites: Compatible with Windows 10 workstations, recent Windows Server OS, or Linux distributions supporting .NET Core. Required applications: GIT and .NET Core 2.2 SDK.
> Installation Process: Covenant uses a modern, cross-platform architecture and does not come with a traditional installer. Installation involves cloning the project git repository and building and running the application.
Section 2.a: Online Installation
> Below are the steps illustrated in Covenant C2's official documentation.
> Starting from your Kali machine, you can clone and cd into your new Covenant package.
> git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/cobbr/Covenant
> cd Covenant/Covenant
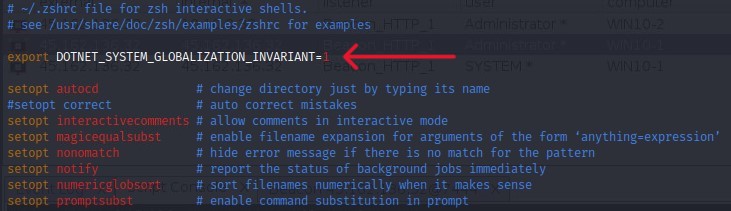
> If you don't add this rule to the zsh script, you'll recieve a "Couldn't find a valid ICU package installed on the system".
> This typically occurs in Dotnet Core projects or packaged Dotnet Core binaries running on Ubuntu due to a missing dependency for Unicode and Globalization support.
> sudo su
> vim ~/.zshrc
> dotnet build
> dotnet run
> This concludes the online installation and you are ready to explore the dashboard in Section 2!
Section 2.b: Offline Kali Installation
> On an online Windows/Mac/Linux machine, run the following commands and save to a zipped folder
> Once you copy you zipped file over to your Kali machine, extract and CD into your Covenant folder.
> If you try to 'dotnet build' your project you'll encounter this error.

> This is where I had trouble with dependencies. .NET is trying to reach out to the internet and download its required Nuget dependencies.
> The dependencies you will need can be downloaded here.
> Once you download these to your online Windows/Mac/Linux, copy them over to Linux and upload them here.
> In covenant, you'll now make two configurations to the nuget.config file. > Config 1 with picture > Config 2 with picture
> dotnet build
> dotnet run
Section 3:Covenant Dashboard Basics
> So once you verify that Covenant is running, let's talk about the dashboard.
> The dashboard is divided into three main sections: Grunts, Listeners, and Tasks.
> Grunts are the agents controlled by the Covenant framework, designed to execute tasks and payloads on compromised hosts, reporting back to the Covenant server.
> Listeners are the endpoints that Grunts connect to. Listeners are responsible for receiving Grunt connections, authenticating them, and relaying commands and responses between the Grunt and the Covenant server.
> Tasks are the actions that Grunts can perform. Tasks are executed on Grunts and can be used to perform actions on the host, such as executing a shell command, uploading a file, or executing a Covenant script.
Section 4: Setting Up Your First Listener